التعريف بقسم الهندسة الكهربائية
الهندسة الكهربائية متغيرة ومتطورة بشكل سريع و تخدم حقول شتى فالتوسع في دور الهندسة الكهربائية أصبح يعكس فاعلية و تطور حقول العمل في مختلف التخصصات و للوصول إلى التميز فقد أعد البرنامج الدراسي ليكون شاملاً وقريباً من متطلبات واحتياجات المجتمع من الطاقة الكهربائية وليكون للطالب بعداً أخر في نضرته للطاقة البديلة و أهميتها في الاستمرارية و المحافظة على البيئة التي تواجهها تحديات جمة بمنطقة الواحات نتيجة تلوث المياه الجوفية و الهواء المصاحبين لإنتاج النفط والغاز وفقر البنية التحتية.
الرؤية
للحصول على مرتبة مميزة في تقديم تعليم عالي الجودة و برامج بحثية مميزة و خدمة مميزة للمجتمع.
الرسالة
لنقدم تعليم حديث في مجال الهندسة الكهربية مع موازنة منطقية بين النظرية و التطبيق مستفيدين من الموقع الجغرافي لأهم حقول إنتاج المياه الجوفية و النفط و محطات الكهرباء و المستقبل الواعد للطاقة الشمسية بالمنطقة حيث السطوع الشمسي و توفر معادن السلكا و الأرض المنبسطة و لنعمل على تخريج مهندسي كهرباء مؤهلين لتلقي مزيداً من العلم قادرين على التطور و مساهمين بفاعلية في خدمة المجتمع.
الأهداف
خريجي قسم الهندسة الكهربائية:
- سينخرطون بشكل جوهري بأعمال الهندسة الكهربائية المختلفة بالقطاعين الخاص والعام بليبيا.
- سيتقدمون في مقدرتهم على تحمل المسئولية والقيادة في عملهم والانخراط في تكنولوجيا متطورة باستمرار وفي تحدي الصعاب الاجتماعية.
- مؤهلين للمساهمة في خدمة المجتمع و العمل التطوعي و التضامني و البيئة و المشاركة في الفعاليات العلمية مع الهيئات الخاصة والعامة.
البرنامج الدراسي
المقررات الدراسية: قسم الهندسة الكهربائية
أعد البرنامج الدراسي لقسم الهندسة الكهربائية ليشمل شعبة هندسة الاتصالات، العدد الكلي للمقررات هو 55 مقرراً و هو ما يعاد 159 وحدة دراسية و شعبة هندسة الطاقة، العدد الكلي للمقررات هو 54 مقرراً و هو ما يعاد 154 وحدة دراسية مصنفة كالتالي:
Ge = General Engineering Sciences
Math = Mathematical
Phys = Physics
Chem = Chemistry
Arb = Arabic
Eng = English
Pol = Political
Ce = Civil Engineering courses
Tw = Technical Writing
Ee = Electrical Engineering
Ie = Engineering Economy
Ms = Material Science
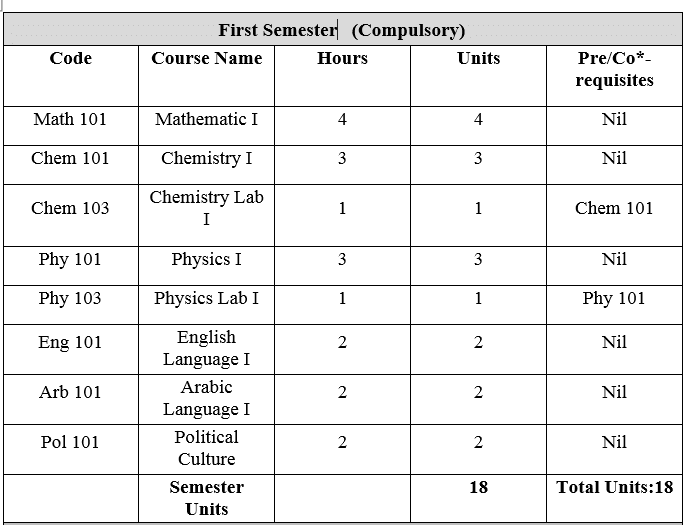
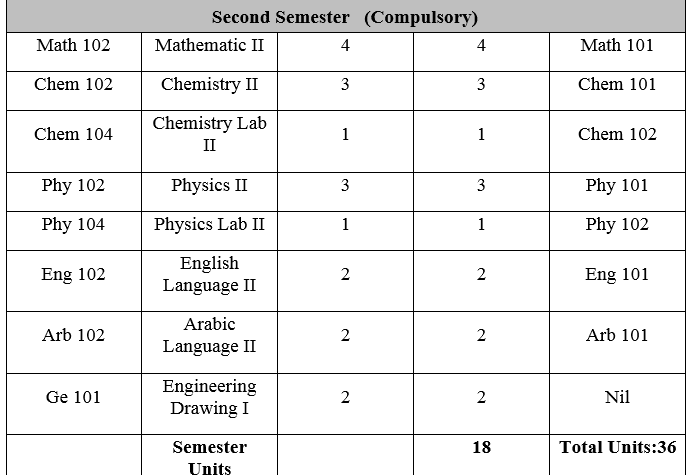
1- المقررات العامة
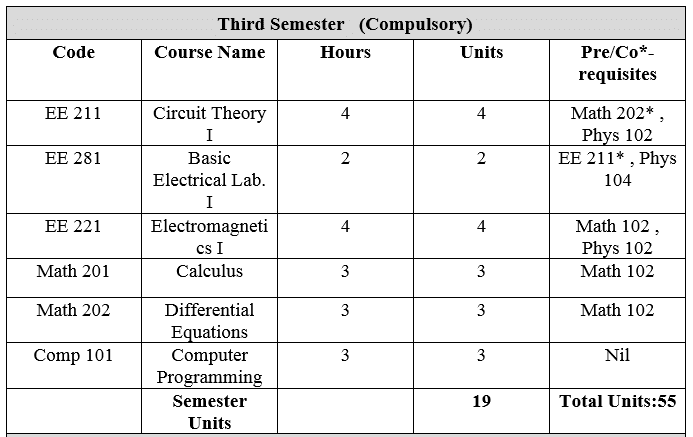
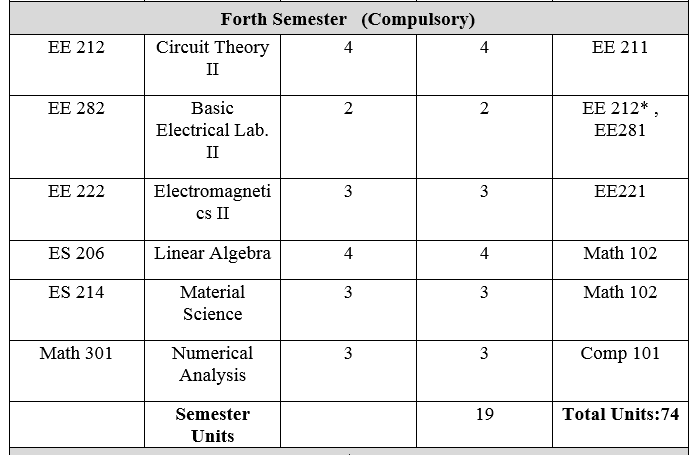
2-شعبة هندسة الإتصالات
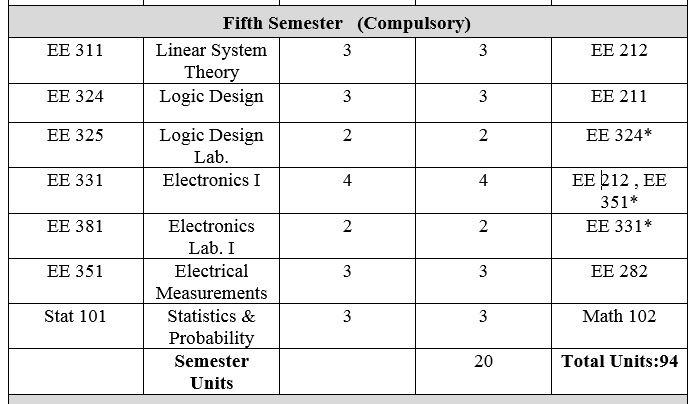
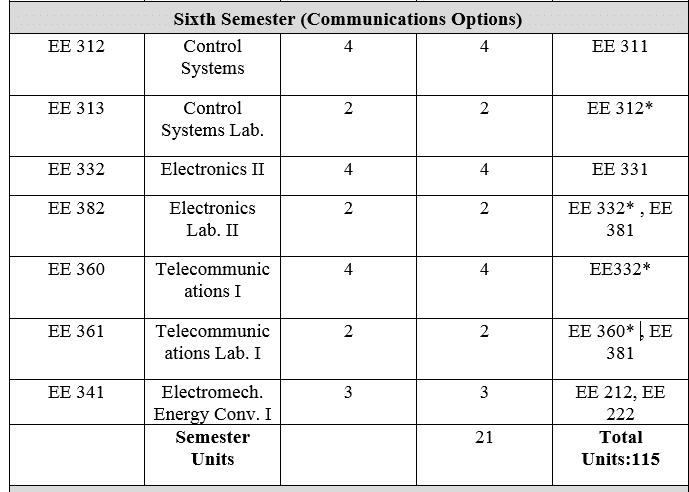
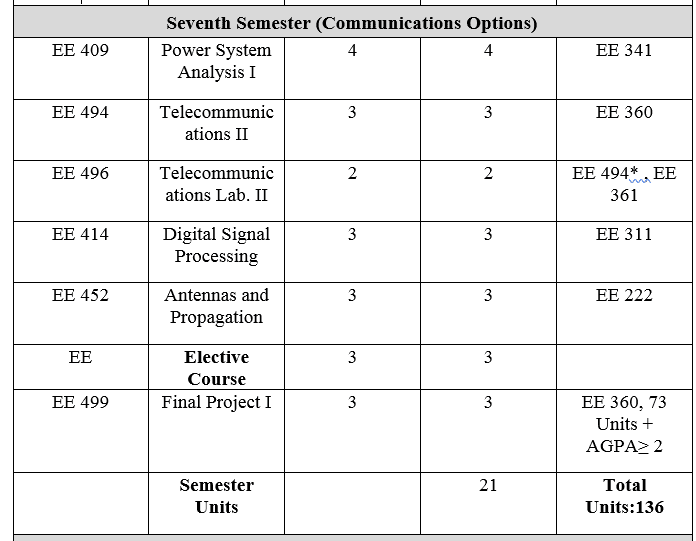
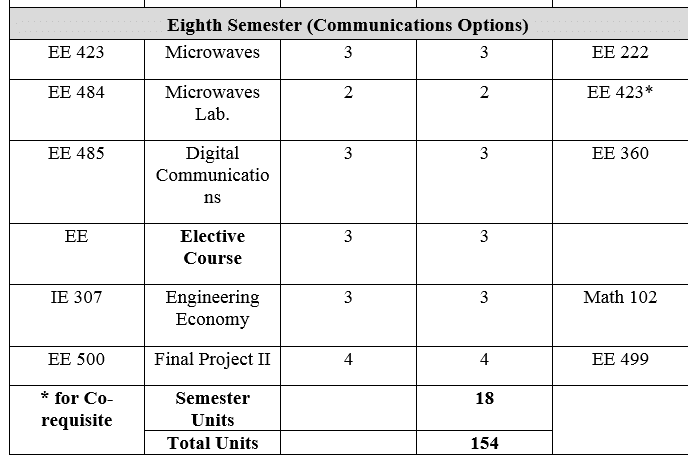
3- شعبة هندسة الطاقة
وصف المقررات
Math 101: Mathematics I
4 Units
Sets, relations, absolute value, functions; Algebra of functions, inverse function, parametric representation of a function. Limits, continuity, derivative, differential, higher derivative, extreme value theorem, intermediate value theorem, Rolle’s Theorem and mean value theorem.
Math 102: Mathematics II 4 Units L,Hopital’s rule. Applications; Maxima and minima, curve tracing, related rates. Conic sections, polar coordinates. Complex number. Definite and indefinite integral. Fundamental theorem. Transcendental function, their derivation and integration. Techniques of integration – Area, length, volume and surface of solid revolution – sequences and series.
Phys 101: Physics I 3 Units Mechanics: Linear and circular motion, Newton Laws of motion, Work, Energy, and Conservation laws of energy. Properties of Mater: Elasticity of matter, Hydrodynamics. Heat and Thermodynamics: Heat, thermodynamics, Laws, ideal gas. Waves and vibrations: Simple harmonic motion, waves, Propagation of waves, standing waves, Properties of optical waves.
Phys 103: Physics Lab I 1 Unit Laboratory work includes experiments on the acceleration of gravity (g), Nook’s Law, Young’s modulus, surface tension, thermal conductivity and specific heat, Newton’s Law of cooling, Sonometer, frequency measurements and the velocity of sound.
Phys 102: Physics II 3Units Electricity and Magnetism: Mirror lenses and their application. Charge, Coulomb’s law, electric field, capacitors and dielectric, current, resistance, electromotive force, electric circuits, magnetic field, magnetic induction , Hall effect. Ampere’s law, circular coils, self-inductance, RC, RL circuits. Magnetic properties of materials. Oscillator’s electromagnetic waves, Maxwell’s equations, Transmission lines, traveling waves, potential and alternating current. Waves and optical, optical waves, reflection and reflection laws, mirrors lenses and their application.
Phys 104: Physics Lab II 1 Unit Verification of Ohms law, Determination of unknown resistance, some measurement using a cathode ray tube, Determination of change magnetic field, Determination of the capacity, Measurement of focal length of an Inaccessible converging law. Measurement of Radii of curvature of converging lens, Measurement of focal length of diverging lens.
Chem 101: Chemistry I 3 Units Atomic structure, periodic table, gas state, thermo chemistry, organic group. Isomerism and fundamental concepts structure and reactivity.
Chem 103: Chemistry Lab I 1 Units
Laboratory rules and techniques, common reagents, chemical equations, cations and anions, reactions of cations and anions, classification of cations and anions into groups, group reagents and group precipitate of cations, identification of cations and anions from simple inorganic compounds.
Chem 102: Chemistry II 3 Units
Radio activity, chemical bonding, covalent bond theory, classification component, element chemical behavior, thermodynamic, electrochemistry, solid state, organic alkene reaction , cycling alkene, alkane, alkyne, alkylhalid, alcohol, aldehyde, ketone with detail study for mechanism reaction, An analytical volumetric, using volumetric apparatus, standard solution, volumetric solution. Titration methods, indicator titration, using acid base, complex compound, oxidation reaction.
Chem 104: Chemistry Lab II 1 Units Volumetric Analysis: use of volumetric apparatus, standard solutions, volumetric calculations, procedure of titrations, indicators, titrations involving acid-base, argentometric, complexometric and oxidation-reduction reactions, determination of strength of unknown samples utilizing the above methods of titration.
Arb 101and102: Arabic Language I and II 2 Unit Each
The courses stress lingual approach to mastery of the language and include the study of basic grammar and selected readings in science and literature.
Eng 101 English I 2 Units Objective: The English I course for first year students has been designed to enable them to communicate in written and spoken English and to develop their ability to deal with concepts used in scientific discussion and writing. Reading comprehension: Topics: Heat energy, atomic structure, ultrasonic, periodic table of elements, computers and some topics of general interest etc. English in communication: Parts of speech, punctuation, simple sentence structure, tenses, passive voice, description of lab ware. Ordinal and cardinal numbers, simple geometry. Laboratory report writing: Lay out of a report: title, abstract, aim, introduction/theoretical background, experiment and materials, procedure, results discussion of results, conclusions, references, appendices.
Eng 102: English II 2 Unit Objectives: The course is for those students who have gone through the first semester. It builds upon the work done in the previous semester and continues with the objectives to enhance the student’s ability to communicate in written and spoken English. The following areas of scientific English are specially stressed upon. Reading comprehension: Topics: Latent heat, Bunsen burner, Spirit burner, computers, Kipp’s apparatus, alloys, metals distillation, fire extinguishers, modern atomic theory, refining petroleum, refrigerators. English in communication: Adjectival clauses, omission of relative pronouns, use of infinitive and gerund, (mathematical concepts: Powers and roots, dimensions of two/three dimensional figures, the use of graphs). Introduction to technical report writing. (Kinds of technical reports: The short informal report, the long informal report, the formal report (their format/structure and style).
Pol 101: Political Culture:
2 Units
Introduction and concepts of political culture, the state (elements, theories, sovereignty, functions, unitary state, welfare state, federal state), Ancient political thought, Contemporary political thought, Comparative Western political systems (reference to USA and UK), Comparative Government and politics, Libyan political system (1952 – 1969), International organization (United Nation UN), Human rights.
Ge 101: Engineering Drawing I: 2 Units Introduction, definitions, terminology and general rules. Tools used in engineering drawing and methods of its use, geometrical processes, engineering curves, kinds of lines and it’s applications, Arabic engineering alphabetic, English engineering alphabetic, drawing scale and dimension, isometric projection, inclined projection, normal projection (isometric and oblique drawing), deduction of third projection, sections and it’s types (complete, half, revolved, partial and its application).
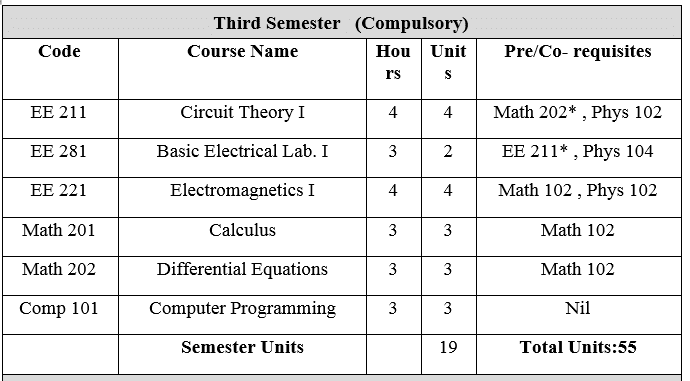
Math 202: Differential Equations 3 Units
Differential equation of the first order and first degree; different forms, non-linear differential equations of the first order; linear differential equations of higher orders; differential operators; linear differential equations with constant coefficients; homogeneous case; method of inverse operator; method of variation of parameters; method of undermined coefficients, Laplace transform; basic theorems, convolution theorem, solution of differential equation by Laplace transform.
Math 203: Linear Algebra 3 Units
Vector spaces, matrices and determinants, simultaneous linear equations, linear transformations, Eigen value problems, canonical forms, numerical linear algebra, linear differential equations, linear programming, inner product spaces applications in various areas such as control theory, Statistics, linear circuit and vibration theory, etc.
Comp 101: Introduction to Computer and Programming: 3 Units
Theoretical Part: Computer definition, computer components, computer languages, flow charts, The steps of solving problems by computer, introduction visual BASIC, variables and constant, arithmetic operations, string operations, comparison operations, logical operations, operators, Control Statements, Arrays, Subroutines, Some of the V.B. Functions, The most important tools and some of their properties and events. Laboratory Part: Work area, menu bar, form, and tool bar, project window, tool box, properties box.
Tw 307: Technical Writing and oral presentation 2Units
Objective: The course is intended to develop the students’ ability on the oral presentation skills and to deal with concepts in scientific discussions and writings. It is to improve their concepts of Technical English enabling them to write Technical Reports, Technical essays as well as Business letters. The course lays stress upon the following areas of technical English:
- Different types of technical reports: The short informal report, the long informal report and the formal report; their format structure and style (Foreword and summary: Organizing main points for Non-specialist readers; Details or discussion: Organizing details for specialist readers; the abstract; conclusions and recommendations, etc.); Feasibility and project report; articles on technical topics and business letters.
- Technical terms of importance to engineering, with emphasis on spelling, and usage in sentences; technical terms used in computer applications.
- Symbols, abbreviations, glossaries, nomenclature, titles and sub-titles, tabular, graphical and pictorial presentation of data and the like, with examples.
- The course also abreast the students with concepts of research. The following main points are stressed upon: Selecting a suitable subject, writing a tentative thesis sentence, developing a preliminary bibliography, – Taking notes, writing précis and paraphrases, developing the first draft, preparing the final documentation notes, formatting the final draft.
Math 203: Linear Algebra 3 Units
Vector spaces, matrices and determinants, simultaneous linear equations, linear transformations, Eigen value problems, canonical forms, numerical linear algebra, linear differential equations, linear programming, inner product spaces applications in various areas such as control theory, Statistics, linear circuit and vibration theory, etc.
EE 211: Circuit Theory I 4 Units
Circuit definitions: Current, Voltage, Power, Independent and dependent sources, Node, Loop, Mesh, Branch, Ohm’s law and Kirchhoff’s laws and their applications on simple circuits. Analysis techniques: Equivalent resistance, Dividers, Source transformation, Superposition, Thevenin’s and Norton equivalent, Maximum power transfer, Nodel analysis, Mesh analysis. Electrical signals: Mathematical and graphical. Representation, Graphical differentiation and integration. Energy storage elements: Capacitors and Inductors. Transient and steady state response: in first order circuits. Transient and steady state response: in second order circuits.
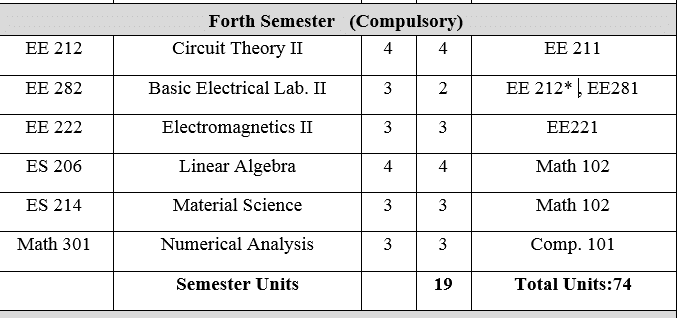
EE 212: Circuit Theory II 4 Units
Review of complex number. Sinusoidal steady state response: phasor, impedance, frequency domain equivalent circuit. Analysis techniques in the frequency domain. Phase shift and phasor diagrams. Average, reactive, and complex power. Effective values and power factor. Frequency response and resonance. Three-phase systems, and three-phase power measurements. Circuit analysis of circuits containing coupled inductors and transformers. Circuit analysis using Fourier techniques. Circuit analysis using Laplace transformation (s-domain circuits).
EE 221: Electromagnetic I 4 Units
Vector algebra: Coordinate systems including general curvilinear. Vector analysis: Differential relations and line, surface and volume integration. Static electric fields: Coulomb’s law, Maxwell’s divergence and curl equations, Capacitance, Energy, Dielectric materials and boundary conditions. Steady magnetic fields: Bio-Savart’s law, Ampere’s law, Maxwell’s divergence and curl equations, Inductance, Energy, Magnetic materials, Boundary conditions and Magnetic circuits.
EE 222: Electromagnetic II 4 Units Boundary value problems for static fields: Solutions by analytical, numerical and analog methods, analytical solutions of Laplaces equation (method of separation of variables). Time varying fields: Maxwell’s equations, Displacement current, Poynting’s theorem and Poynting vector, Faraday’s law, Ampere’s circuital law. Propagation of uniform plane waves: Wave equation and description of uniform plane wave, Plane wave propagation in perfect dielectric and conducting media, Skin effect, Eddy currents, Group velocity, Time averaged Poynting vector and Time averaged energy densities in the electric and magnetic fields, Reflection and refraction of waves.
EE 281: Circuits Laboratory I 2 Units
Familiarization with the laboratory equipments. Verification of Kirchhoff’s laws and equivalent resistance. Dividers and their application in meter-range extensions. Superposition and reciprocity theorems. Thevenin’s and Norton’s equivalents and the maximum power transfer theorem. Different methods for measuring resistance. Use of the oscilloscope for displaying and measuring electrical signals. Charge and discharge characteristics of capacitors.
EE 282: Circuits Laboratory II 2 Units
Transient and steady state response of first order circuits. Transient and steady state response of second order circuits. Phase and power measurements. Frequency response and resonance. Two port parameters-measurements. Fourier analysis and synthesis of electrical signals. Low pass, high pass, band pass and band-stop filters-design and testing. Three phase measurements (voltage, current and power).
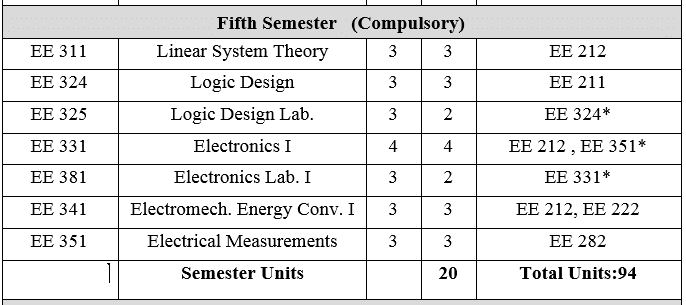
EE 311: Linear System Theory 3Units Classification of systems. Continuous-time systems. Block diagram, signal flow graph. Concept of state space model of linear systems. Solution of state equations. The concept of controllability and observability. Realization of state space model. Introduction to the analysis of discrete-time systems. Difference equations, Z-transformation and its application to discrete systems, State space model of linear discrete systems, Controllability and Observability, Solution of systems.
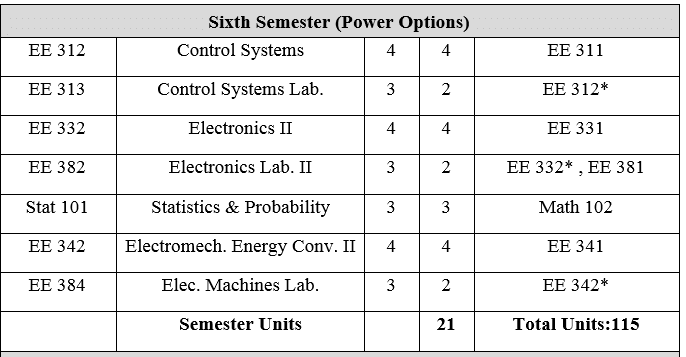
EE 312: Control Systems 3 Units Mathematical notations and definitions. Mathematical modeling of physical systems and examples. Closed-loop control systems: Characteristics. Time domain analysis of control systems. Stability of linear systems: Specifications. Design of linear feedback control systems.
EE 324: Logic Design 3 Units
Various number systems. Boolean algebra and logic gates. Simplification of Boolean functions. Combinational logic. Binary parallel adder. Decimal adder. Magnitude comparator. Decoders and multiplexers. Synchronous sequential logic: Introduction to flip-flops, RS flip-flop, JK flip-flops, T flip-flop and D flip-flop, Registers, parallel register, shift registers, design of logical circuits using flip flops and registers, counters, memory: ROM, RAM. Hazards.
EE 325: Logic Design Laboratory 2Units
Binary and decimal numbers. Digital logic gates. Simplification of Boolean functions. Combinational circuits. Code converters. Design with multiplexers, adders and subtractors. Flip-flops. Sequential circuits. Counters.
EE 331: Electronics I 4 Units Introduction to PN junction theory. Diode operation, characteristics, large and small signal models. Analysis of diode circuits. Zener diode. Diode applications such as clipping damping, rectification, regulation, function generation… etc. Diode capacitance. BJT theory: Operation, characteristics, large and small signal models. BJT biasing. CB, CE and CC amplifiers. FET theory: Operation, characteristics, small signal model. FET biasing, circuits and applications.
EE 332: Electronics II 4 Units
Power amplifiers: Classification graphical analysis, transistor limitation, class B push-pull and class C tuned power amplifiers, heat sinks. Frequency response of amplifiers: Multistage amplifiers, low frequency and high frequency response of BJT and FET, Gain-Bandwidth product, input and output impedance. Difference amplifiers, operational amplifiers: Ideal and practical Op-Amp, biasing, parameters and various configurations, balancing techniques. Applications of Op-Amp: Active filters using Op-Amp. Feedback amplifiers: Principles of negative feedback and its advantages, effect of feedback on gain stability, dynamic response, input and output impedances. Sinusoidal Oscillators: Principles of oscillation, various types of Oscillator’s circuits: Tuned circuit, RC, Wien Bridge, Hartley, Colpitts and Crystal oscillators.
EE 341: Electromechanical Energy Conversion I 3 Units
Single and polyphase transformers: equivalent circuits of transformers, parallel operation of transformers. Basic principles of electromechanical energy conversion. Basic principles of D.C. and A.C. machines. EMF generator and MMF for D.C and A.C. machines. Steady state performance of D.C. machines. Types of D.C. machines. Armature reaction. D.C. generator and motor characteristics, interpoles and compensating winding.
EE 342: Electromechanical Energy Conversion II 3 Units
Polyphase synchronous machines: Steady state analysis. Polyphase induction machines: Steady state analysis. A.C. machine transients. Single phase machines.
EE 351: Electrical Measurements 3Units Fundamentals: Units, significant figures, errors, statistical evaluation of measured data, principles of measurement. Instrumentation: Electromechanical and electronic meters, meter features, oscillograph and oscilloscope. Measurements: Voltage, current, resistance, induction, capacitance and energy.
EE 381: Electronics Laboratory I 2Units
Diode characteristics and parameters. Diode response to large and small signals. Diode clipping and damping circuits. Diode application in rectifier circuits. Zener diode characteristics and application as a voltage regulator. Transistors characteristics, and large signal parameters. Transistor small signal parameters. Design and testing of CE amplifiers.
EE 382: Electronics Laboratory II 2 Units
Design of CE amplifier and frequency response plot. Emitter-follower circuit and Darlington pair connections of BJT. JFET characteristics and parameters. Common-source amplifiers. Design of RC coupled amplifier with and without feedback. Operational amplifier (Op-Amp) as a basic building block in the design of analog systems. Design of 2nd order active RC filters using Op-Amp: Low pass, High pass, Band pass, Band exclude filters. Design of sinusoidal oscillator circuits using Op-Amp. Design of a regulated power supply systems.
EE 384: Electronics Machine Laboratory 2 Units
Three phase transformer. D.C. motors and generators (shunt, series and compound). Polyphase synchronous generators. Single phase induction motors (capacitor start and run types). Speed control of polyphase induction motors.
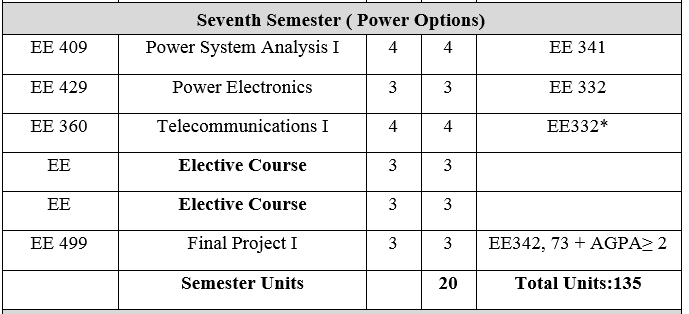
EE 409: Power System Analysis I 4 Units
Inductance of transmission lines. Capacitance of transmission lines. Current and voltage relations on a transmission line. Generalized circuit constants. Circle diagrams. Structure of power systems. Power system representation. Power system components and their equivalent circuits. Symmetrical three phase faults and components.
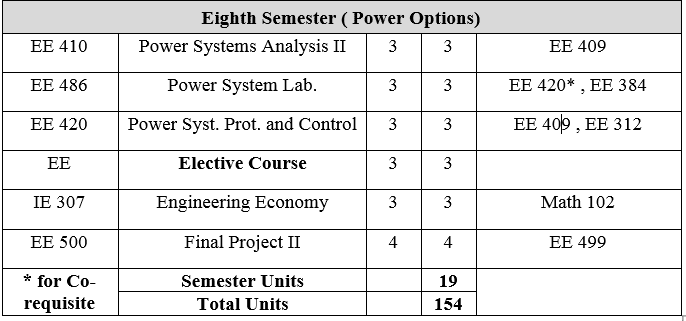
EE 410: Power System Analysis II 4Units
Symmetrical components. Unsymmetrical components. Load flow analysis. Methods controlling MW and MVAR flows. Stability of power systems. Economical operation of power system.
EE 411: Digital Control Systems 3 Units
Basic of digital control system modeling. Principles of signal conversion: Analog to Digital and Digital to Analog conversions, sampling process, timing considerations, and properties of zero and first order hold operations. Discrete systems modeling: Linear difference equations, Z-transforms, mapping between S and Z domains, inverse Z-transform. Z-plane analysis of discrete time systems: Transient response analysis and steady state error analysis, stability, Jury’s stability test, root-locus analysis, pole assignment. Bilinear transformations: Frequency response analysis, lead, lag and lead-lag compensators. PID controllers. State space design methods.
EE 412: Information Theory & Statistical Communication 4 Units
Information Theory: Information, information entropy, information rate redundancy, Shannon’s theorem for information rate in noisy channels. Introduction to coding: Coding matched to entropy of message, error detection and correction, parity check, algebraic code and error syndrome. Digital communications: Data communications, ASK, FSK, PSK and M-ary data communications system. Decision theory: Optimum detection of signals in the white noise, matched filtering. Fading channels: Diversity techniques, line of sight and troposcatter link design.
EE 360: Telecommunication I 4 Units
Introduction to signals and waveforms: Signals, waveforms, analysis using Fourier series and integral, power and energy spectral densities, filtering of signals, filter response, convolution and deconvolution, correlation between waveforms, autocorrelation and power relationships. Modulation techniques: Modulators and detectors for AM, DSB-C, DSB-SC, SSB and comparison between the different techniques. Angle and frequency modulation: Narrow and wide band FM systems, pulse modulations (PAM, PPM and PWM). Multiplexing: Frequency division multiplexing (FDM), time division multiplexing (TDM). Introduction to pulse code modulation (PCM). Signal to noise ratio concepts and its calculations.
EE 420: Power System Protection and Control 3 Units
Structure of power systems, classification of power system protection and neutral earthing. Basic terms used in PSP theory and practice, methods of discriminations, main components of PSP. Non directional and directional over current protection. Distance protection and differential protection. Transformer Buchholz protection. Automatic circuit reclosing, restoration and under frequency load shedding. Power frequency control: reactive power-voltage control, voltage control in electrical networks, computerized control and dispatch centers.
EE 422: Radio, T.V. and Radar 3 Units
Radio circuits and parameters: AM transmitter, AM super-heterodyne receiver, FM transmitter, FM receiver. Television: Principles of black and white TV systems, B/W TV transmitter, B/W TV receiver, principles of color TV systems, color TV transmission, color TV reception. Radar: Principles of radar, CW and FM radar, pulse radar, transmitter transmission track, antenna, receiver, inductor of a pulsed radar, MIJ radar.
EE 423: Microwaves 3 Units Distributed circuit analysis of TEM mode transmission lines. Rectangular and circular waveguides. Different transmission modes of TE and TM. Impedance transformation and matching techniques. Passive microwave devices: Microwave resonators and filters, microwaves integrated circuits, PJN diodes, Gunn diode, ferrite isolator, chokes. scattering matrix. Microwaves measurements.
EE 429: Power Electronics 3 Units
Large current electric components: Diodes, thyristors, triacs. High power converters and special converters for D.C. transmission. High frequency heating: induction and dielectric influence of converters on supply network and special applications.
EE 430: Power Generation 3 Units
Basic contemporary energy resources. Power generation in power system: Function of particular types of power stations, peak load and standby power plants. Fundamental knowledge of thermodynamics and thermodynamics cycles. Thermal power stations: working cycles, fuels and generation efficiency, steam turbines and internal combustion plants, steam generators, hydropower stations and direct energy conversion. Electric power utilization, illumination, industrial and commercial applications of electric power.
EE 431: Pulse and Digital Circuits 3 Units
Nonlinear wave shaping, inverter design. Transient behavior of circuits containing a single reactive element. Circuit design of DL, RTL, DTL, TTL, ECL and CMOS logic gates. Regenerative switching and timing circuits.
EE 432: Integrated Electronics 3 Units Integrated circuit fabrication and design, logic families, design and layout, memories and LSI techniques and applications. Linear integrated circuits. Digital to Analog and Analog to Digital conversion.
EE 434: Solar Energy 3 Units
Solar radiation, solar constant, spectral distribution, radiation on horizontal surfaces and tilted surfaces. Available solar radiation, pyraheliometers and pyranometers, duration, of sunshine, estimation of clear sky radiation, atmospheric attenuation of solar radiation, beam and diffuse components of radiation (daily or monthly). Solar cells: PN junction cell characteristics and equations, types of solar cells, solar cell output characteristics and limitations, photovoltaic array consideration, photovoltaic power system considerations, design of stand-alone PV system.
EE 440: Transmission Line Design 3Units Electrical characteristics of a transmission line. Mechanical characteristics of a transmission line. Insulators, brushings, and underground cables.
EE 442: Medical Electronics 3 Units
Brief introduction to cell, tissue and physiological system, genesis of steady potential, action potential, propagated nerve impulses, volume conductor field, electrocardiography, electrocephalography and electromyography. Transducers for recording biological events. Amplifiers for biological signal recording. Instrumentation for electrocardiographic, electrocephalographic and electromyographic signals. Detection of physiological events by impedance techniques. Magnetocardiograph, echocardiograph, casioscope, blood pressure recorder, telecorder and X-ray, display and recording devices for biological signals. Diathermy. Pacemakers and artificial aids, standardization of medical equipments.
EE 449: Control Instrumentation 3 Units
General structure of control systems, physics of control components, mechanical and electrical quantities equivalencies. Transducers of non-electrical quantities. Typical control components. Design of control system in light of relative merits of various control components.
EE 450: High Voltage 3 Units
Application of high voltage. Insulation equivalent circuit and parameters: Resistance, capacitance, polarization, absorption factor, loss factor, permittivity, resistivity, electrical strength. Field distribution in insulation systems, grading, resistively and capacitively controlled field distribution. Electrical discharge in gases, liquids and solids. Electrical strength of insulation systems. Overvoltages in power systems. Impulse voltage. Insulation coordination idea.
EE 451: Electronic Instrumentation 3 Units
Electronic analog and digital voltmeters, electronic multimeters, electronic component meters, Q-meters, special purpose electronic meters. Introduction to vector voltmeters and vector impedance meters, single and double beam cross, applications of CROS. Storage, sampling and digital readout oscilloscopes, oscillators, pulse generators, function generators, different types of wave analyzers simple frequency counter. Measurement of periods, different types of transducers, measurements of strain, displacement, temperature, light and radiation. Use of electronic instrumentation in scientific measurements.
EE 452: Antenna and Propagation 3 Units
Review of relevant electromagnetic theory: Maxwell’s equations, boundary conditions, Poynting vector and power flow, wave equation, time varying plane, waves in various medias. The far-field expressions of actual and equivalent source antennas: The Sratton-Chu solution, vector potential, the Schelkunoff field equivalence principles. The far-field basic properties of antenna: Radiation pattern, gain, directivity, reciprocity, polarization, impedance, antenna’s noise temperature and bandwidth, aperture, current elements. Different types of antennas: Ideal dipole, short, dipole, long dipole, folded dipole, loop antenna, helical (helix) antenna, horn antenna, array antennas, parasitic elements in antennas and Yagi-Uda antenna. Propagation: The basic of ground waves, tropospheric and ionospheric propagation.
EE 453: Antenna Laboratory 3 Units Familiarization with antenna types, definitions and laboratory equipments. Description the physical length and the electrical length of an antenna. Plotting radiation patterns: calculating bandwidth and examining the polarization of different types of antennas: half-wave dipole, half-wave folded dipole, vertical end fed antenna (monopole antenna), parasitic arrays antenna (source, reflector and directors), Yagi-Uda antenna, slot antenna… etc. Familiarization with the matching stubs. Measurements of Gain and Standing wave ratio (SWR) of above antennas.
EE 459: Real Time Computer Appl 3 Units
The role for one line, real time computer in engineering and management. Hardware of real time computers. Processors, storage, men-machine terminals interface, digital and analog inputs. General configuration of computers. Software of real time computers: Operation systems, languages. Programming real time computers. Parameters of existing real time minicomputers.
EE 460: Design of Electrical Systems 3 Units
Types of electrical systems. Electric power systems. Connection schemes, dimensioning conditions, normal load and fault conditions. Thermal effect of normal and load current, power demand and calculations. Thermal and dynamic effect of short circuit current rupturing capacity, circuit opening devices, loss calculations, power factor improvement, reliability and economics factor. Lighting design, domestic and industrial electric systems. Electric shock protection.
EE 470: Substation Equipment 3 Units Classification of substation equipment and general requirements, substation equipments. Short circuit level and circuit breaker rating. Circuit interruption theory and process. Different types of circuit breakers. Reactive power compensation, earthing and testing of substation.
EE 361: Telecommunications Laboratory I 2 Units
LC circuits: Tuned circuits and coupled tuned circules. Frequency analysis of periodic and modulated waveforms: Amplitude Modulation (AM), Double Sideband Full Carrier Modulation (DSB-FC), Single Sideband Modulation (SSB), Frequency Modulation (FM), Pulse Amplitude Modulation (PAM), Pulse Width Modulation (PWM), Pulse Code Modulation (PCM), Delta and Sigma Modulations. Sampling and receiver measurements.
EE 480: Electric Power Utilization 2 Units
Electrical motors for industrial drives, selection of motors and motors for particular services. Electric heating and welding: Types of ovens and furnaces, and types of welding. Electrolytic and electrometallurgical processes. Illumination: basic calculations, types of devices. Electric traction: calculations based on speed/time graphs, types of traction, speed control and electrical braking. Storage batteries: Types and constructional features, charging and discharging, maintenance.
EE 484: Microwaves Laboratory 2 Units
VSWR, reflection coefficient and impedance measurements, Smith chart. Frequency and guide wavelength measurements. Directional coupler, hybrid T and ferrite isolator measurement. PJN diode modulator and Gunn diode oscillator measurements.
EE 491: Control Laboratory 2 Units
Analog computers: Passive and active computing components, introduction to analog technique and its application to simulation of control systems, simulation of open-loop and closed-loop control systems, time scaling and magnitude scaling. Servomechanism: Motor characteristics and error channel investigation in modular servo-type MS-150 system, simple position control system (open-loop and closed-loop), simple speed control system, dead band and overshoot as functions of gain.
EE 492: Microprocessors and Applications 3 Units
Review of logic gates and memory devices. Introduction to computers, microcomputer structure and operation, microprocessor hardware. Programming the microprocessor.
EE 493: Microprocessors Laboratory 2 Units
Familiarization with microcomputer kit, simple arithmetic addition and subtraction programs, logical operations, decimal and hexadecimal arithmetic programs. Input/output monitor interface, delay routines, stepper motor speed and direction control, monitoring analog to digital converters, waveform generation using digital to analog conversion.
EE 494: Telecommunications II 3 Units Probability and random variable introduction, conditional probability and statistical independence, probability distribution and density function, transformation of random variables. Autocorrelation and power spectra. Noise: Thermal noise, equivalent noise bandwidth, noise in cascade systems, noise effect in modulation systems, AM detection performance, angle modulation detection performance, noise in PCM, performance of complete systems, digital system comparison. Digital communications: Basic PCM encoding and quantization, baseband encoding forms, RF digital modulation methods, differential and quadriphase shift keying, data communication. Information and channel capacity, measurement of information/communication channels, discrete communication channels, continuous channels.
EE 495: Telephony and Teletraffic 3 Units General description of the public telephone network. Telephone terminals. CCITT recommendations. Analog telephone networks. Evolving digital networks. Voice band data transmission. Space division switching. Time division switching. PCM switching. Network synchronization. Teletraffic of telephone networks.
EE 497: Electroacoustics 3 Units
Basics of electroacoustic, physical quantities of sound waves, the relationship between excess pressure and particle velocity of a plane sound wave in air, audible perception and the subjective value. Masking effect, spherical waves, specific acoustic impedance, acoustic intensity and energy density. Analog between mechanical and electrical circuit, the electromechanical analogy for acoustic system, electro-acoustical analogy for acoustic system electro acoustical analogy. Electroacoustic transducers classification: electromagnetic transducers (electrodynamics transducers and moving iron plate transducer), Electrostatic transducers (condenser transducer and PIEZO electric transducer. Microphones (μ-phones): technical characteristics, moving coil electromagnetic μ-phone, carbon μ-phone, capacitive μ-phone, dynamic ribbon μ-phone, PIEZO electric μ-phone. Loudspeakers (LS): simple theory of LS, moving coil LS.
EE 214: Material Science 3 Units
Simplified atomic theories, energy bands, periodic table, chemical bonds, structure of materials, Dielectric properties of materials: dielectric susceptibility of different types, temperature and frequency dependence of dielectric constant, Ferro-electric material and their applications. Magnetic properties of materials: magnetization, classification according to magnetic properties, Ferro-magnetism, hard and soft magnets, permanent magnets, ferrites. Conductivity: theory of specific resistance, temperature dependence, super conductivity. Semiconductors and devices, energy bands.
IE 307: Engineering Economy 3 Units
A study of methods for determining the comparative financial desirability of engineering alternatives. Topics include: interest, time value of investment, break even and minimum cost analysis, replacement analysis, and depreciation analysis. The computer use in solving some problems in engineering economy.
CE 598: Project methods and proposal 2Units
Oil field methods, data gathering, sampling methods, data preparation and classification, data presentation, spread sheets calculation and analysis of data, project proposal methods, referencing methods, software’s practices, project methods, and project report structure, project writing formats, project proposal preparation and presentation.
CE 599: Graduation Project 4Units
The class objective is to provide experience in the application of engineering principles to the solution of a specific problem in Electrical and electronic Engineering. Students are required to select a topic and prepare a proposal, including a work programmed for a project to be undertaken under the supervision of a faculty member. Projects may include laboratory or field experiments, design problems, computer analysis or literature reviews. Students are expected to prepare a typewritten report and to make an oral presentation of their project.
