التعريف بقسم الهندسة المدنية
الهندسة المدنية من أقدم التخصصات الهندسية وهي معنية بالتحكم في بيئة و معيشة الإنسان و التخطيط و التصميم لإنشاء الانظمة والمرافق مثل المباني و الجسور و الطرق و المطارات و أنظمة النقل و التركيبات البحرية و الشاطئية و أنظمة التحكم بالتلوث و الفيضانات بالأنهار و البحيرات و أنظمة الملاحة الارضية و السدود و مشاريع مصادر المياه و أنظمة الري و الصرف و أنظمة ادارة المخلفات و أنظمة حماية البيئة. لهذه الاغراض آنفة الذكر وجهت المقررات لتقديم تدريب عام للطالب في تخصصات الهندسة المدنية و لتمكينه من القدرة على التكيف مع التطور السريع للاحتياجات التكنولوجية والعلمية بمنطقة الواحات و ليبيا عموماً.
الرؤية
للحصول على مرتبة مميزة في تقديم تعليم عالي الجودة و برامج بحثية مميزة و خدمة مميزة للمجتمع.
الرسالة
لنقديم تعليم حديث في مجال الهندسة المدنية مع موازنة منطقية بين النظرية و التطبيق مستفيدين من الموقع الجغرافي لأهم حقول إنتاج المياه الجوفية و النفط و المستقبل الواعد للطاقة الشمسية بالمنطقة و ليبيا و لنعمل على تخريج مهندسين مؤهلين لتلقي مزيداً من العلم قادرين على التطور و مساهمين بفاعلية في خدمة المجتمع.
الأهداف
خريجي الهندسة المدنية:
- سينخرطون بشكل جوهري بأعمال الهندسة المدنية المختلفة بالقطاعين الخاص والعام بليبيا.
- سيتقدمون في مقدرتهم على تحمل المسئولية والقيادة في عملهم والانخراط في تكنولوجيا متطورة باستمرار وفي تحدي الصعاب الاجتماعية.
- مؤهلين للمساهمة في خدمة المجتمع و العمل التطوعي و التضامني و البيئة و المشاركة في الفعاليات العلمية مع الهيئات الخاصة والعامة.
البرنامج الدراسي
المقررات الدراسية: قسم الهندسة المدنية
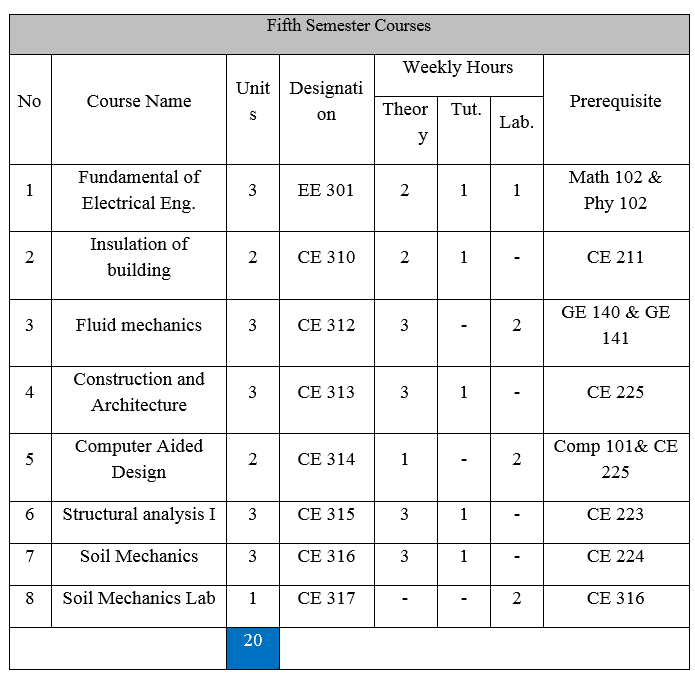
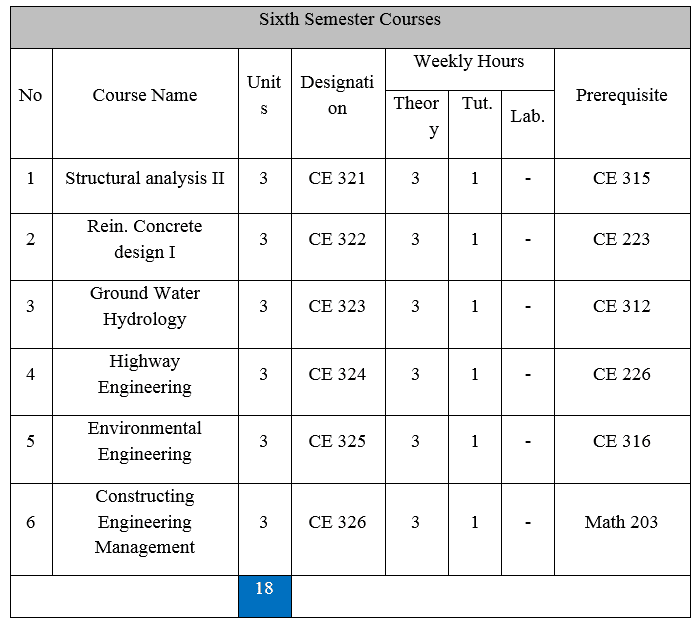
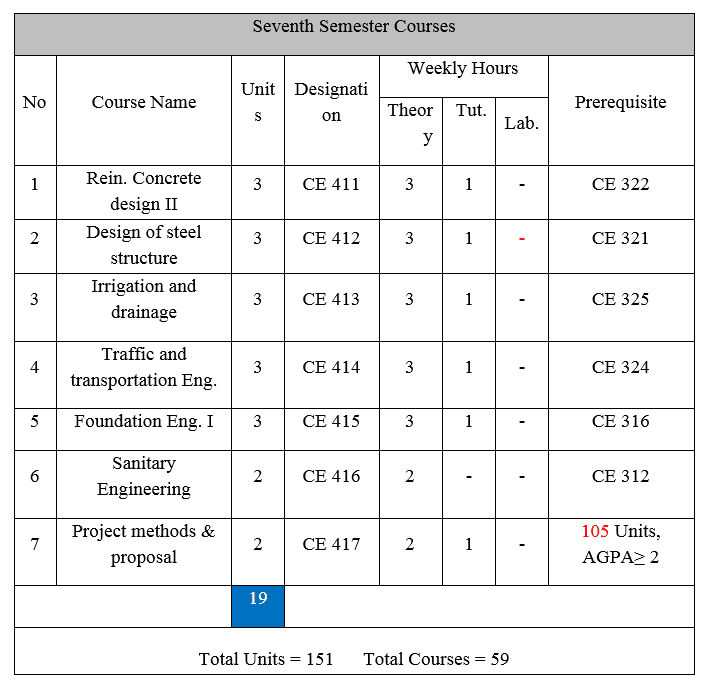
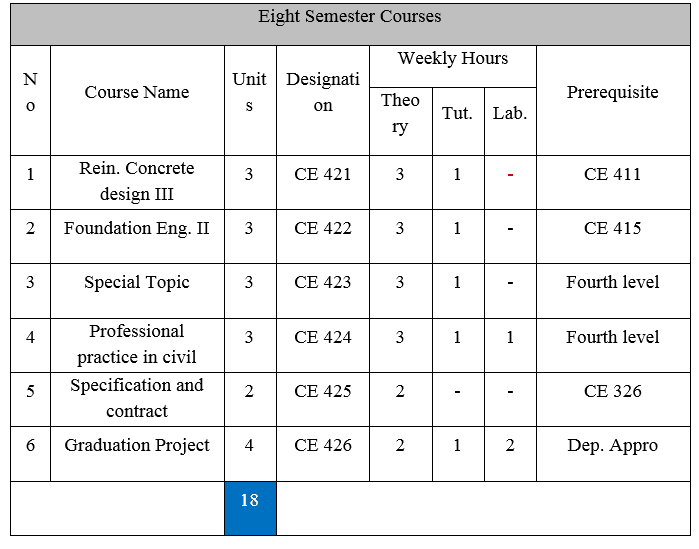
يوازن البرنامج الدراسي لقسم الهندسة المدنية بين الجزء النضري والتطبيقي. بعدد كلي للمقررات هو 59 مقرراً و هو ما يعاد 151 وحدة دراسية مصنفة كما يلي:
Ge = General Engineering Sciences
Math = Mathematical
Phys = Physics
Chem = Chemistry
Arb = Arabic
Eng = English
Pol = Political
Ce = Civil Engineering courses
Tw = Technical Writing
Ee = Electrical Engineering
وصف المقررات
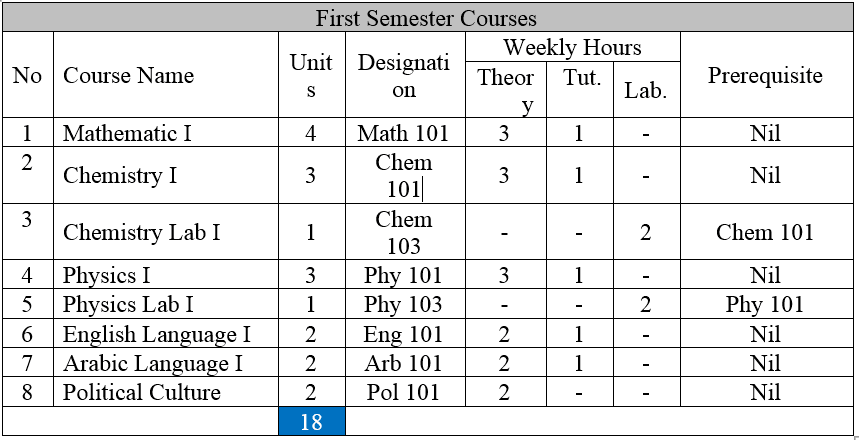
Math 101: Mathematics I 4 Units
Sets, relations, absolute value, functions; Algebra of functions, inverse function, parametric representation of a function. Limits, continuity, derivative, differential, higher derivative, extreme value theorem, intermediate value theorem, Rolle’s Theorem and mean value theorem.
Math 102: Mathematics II 4Units
L,Hopital’s rule. Applications; Maxima and minima, curve tracing, related rates. Conic sections, polar coordinates. Complex number. Definite and indefinite integral. Fundamental theorem. Transcendental function, their derivation and integration. Techniques of integration – Area, length, volume and surface of solid revolution – sequences and series.
Phys 101: Physics I 3 Units
Mechanics: Linear and circular motion, Newton Laws of motion, Work, Energy, and Conservation laws of energy. Properties of Mater: Elasticity of matter, Hydrodynamics. Heat and Thermodynamics: Heat, thermodynamics, Laws, ideal gas. Waves and vibrations: Simple harmonic motion, waves, Propagation of waves, standing waves, Properties of optical waves.
Phys 103: Physics Lab I 1Unit
Laboratory work includes experiments on the acceleration of gravity (g), Nook’s Law, Young’s modulus, surface tension, thermal conductivity and specific heat, Newton’s Law of cooling, Sonometer, frequency measurements and the velocity of sound.
Phys 102: Physics II 3Units
Electricity and Magnetism:
Mirror lenses and their application. Charge, Coulomb’s law, electric field, capacitors and dielectric, current, resistance, electromotive force, electric circuits, magnetic field, magnetic induction , Hall effect. Ampere’s law, circular coils, self-inductance, RC, RL circuits. Magnetic properties of materials. Oscillator’s electromagnetic waves, Maxwell’s equations, Transmission lines, traveling waves, potential and alternating current. Waves and optical, optical waves, reflection and reflection laws, mirrors lenses and their application.
Phys 104: Physics Lab II 1 Unit
Verification of Ohms law, Determination of unknown resistance, some measurement using a cathode ray tube, Determination of change magnetic field, Determination of the capacity, Measurement of focal length of an Inaccessible converging law. Measurement of Radii of curvature of converging lens, Measurement of focal length of diverging lens.
Chem 101: Chemistry I 3Units
Atomic structure, periodic table, gas state, thermo chemistry, organic group. Isomerism and fundamental concepts structure and reactivity.
Chem 103: Chemistry Lab I 1Units
Laboratory rules and techniques, common reagents, chemical equations, cations and anions, reactions of cations and anions, classification of cations and anions into groups, group reagents and group precipitate of cations, identification of cations and anions from simple inorganic compounds.
Chem 102: Chemistry II 3 Units
Radio activity, chemical bonding, covalent bond theory, classification component, element chemical behavior, thermodynamic, electrochemistry, solid state, organic alkene reaction , cycling alkene, alkane, alkyne, alkylhalid, alcohol, aldehyde, ketone with detail study for mechanism reaction, An analytical volumetric, using volumetric apparatus, standard solution, volumetric solution. Titration methods, indicator titration, using acid base, complex compound, oxidation reaction.
Chem 104: Chemistry Lab II 1 Units
Volumetric Analysis: use of volumetric apparatus, standard solutions, volumetric calculations, procedure of titrations, indicators, titrations involving acid-base, argentometric, complexometric and oxidation-reduction reactions, determination of strength of unknown samples utilizing the above methods of titration.
Arb 101and102: Arabic Language I and II 2 Unit
The courses stress lingual approach to mastery of the language and include the study of basic grammar and selected readings in science and literature.
Eng 101 English I 2 Units Objective: The English I course for first year students has been designed to enable them to communicate in written and spoken English and to develop their ability to deal with concepts used in scientific discussion and writing. Reading comprehension: Topics: Heat energy, atomic structure, ultrasonic, periodic table of elements, computers and some topics of general interest etc. English in communication: Parts of speech, punctuation, simple sentence structure, tenses, passive voice, description of lab ware. Ordinal and cardinal numbers, simple geometry. Laboratory report writing: Lay out of a report: title, abstract, aim, introduction/theoretical background, experiment and materials, procedure, results discussion of results, conclusions, references, appendices.
Eng 102: English II 2 Unit
Objectives: The course is for those students who have gone through the first semester. It builds upon the work done in the previous semester and continues with the objectives to enhance the student’s ability to communicate in written and spoken English. The following areas of scientific English are specially stressed upon. Reading comprehension: Topics: Latent heat, Bunsen burner, Spirit burner, computers, Kipp’s apparatus, alloys, metals distillation, fire extinguishers, modern atomic theory, refining petroleum, refrigerators. English in communication: Adjectival clauses, omission of relative pronouns, use of infinitive and gerund, (mathematical concepts: Powers and roots, dimensions of two/three dimensional figures, the use of graphs). Introduction to technical report writing. (Kinds of technical reports: The short informal report, the long informal report, the formal report (their format/structure and style).
Pol 101: Political Culture: 2 Units
Introduction and concepts of political culture, the state (elements, theories, sovereignty, functions, unitary state, welfare state, federal state), Ancient political thought, Contemporary political thought, Comparative Western political systems (reference to USA and UK), Comparative Government and politics, Libyan political system (1952 – 1969), International organization (United Nation UN), Human rights.
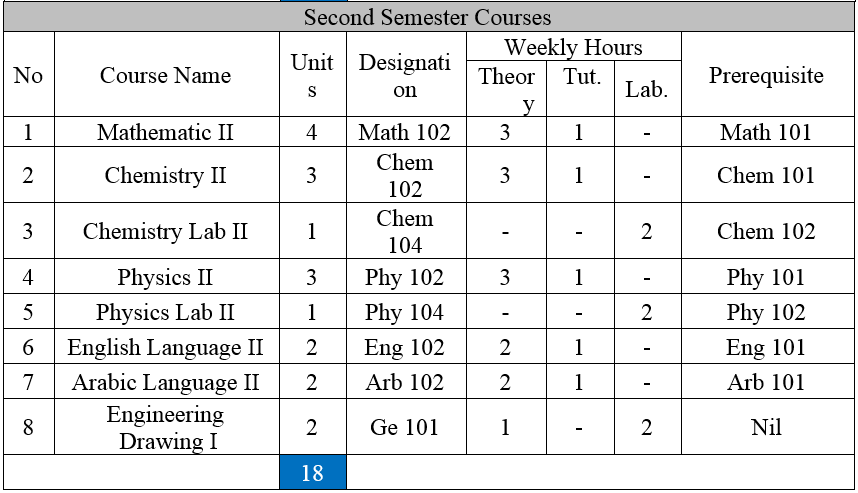
Ge 101: Engineering Drawing I: 2 Units
Introduction, definitions, terminology and general rules. Tools used in engineering drawing and methods of its use, geometrical processes, engineering curves, kinds of lines and it’s applications, Arabic engineering alphabetic, English engineering alphabetic, drawing scale and dimension, isometric projection, inclined projection, normal projection (isometric and oblique drawing), deduction of third projection, sections and it’s types (complete, half, revolved, partial and its application).
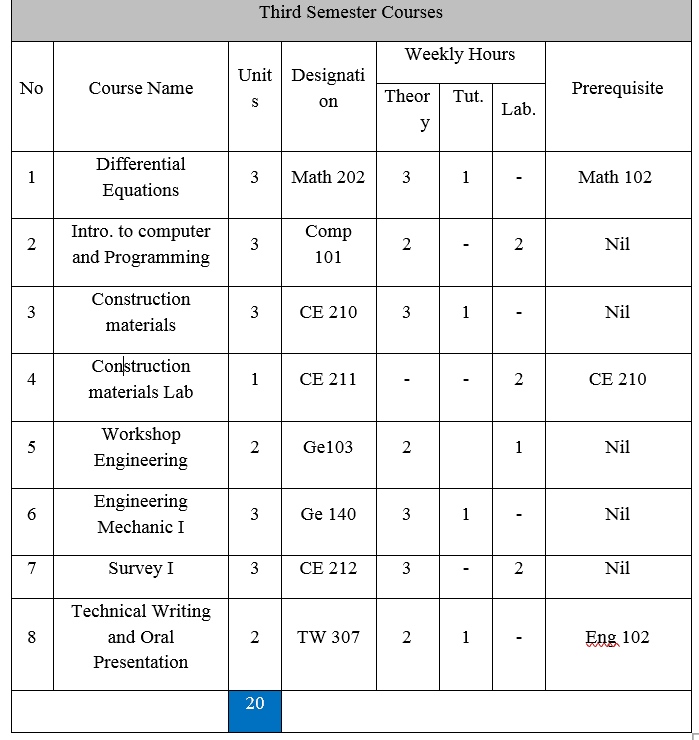
Math 202: Differential Equations 3Units
Differential equation of the first order and first degree; different forms, non-linear differential equations of the first order; linear differential equations of higher orders; differential operators; linear differential equations with constant coefficients; homogeneous case; method of inverse operator; method of variation of parameters; method of undermined coefficients, Laplace transform; basic theorems, convolution theorem, solution of differential equation by Laplace transform.
Comp 101: Introduction to computer and Programming: 3 Units
Theoretical Part: Computer definition, computer components, computer languages, flow charts, The steps of solving problems by computer, introduction visual BASIC, variables and constant, arithmetic operations, string operations, comparison operations, logical operations, operators, Control Statements, Arrays, Subroutines, Some of the V.B. Functions, The most important tools and some of their properties and events. Laboratory Part: Work area, menu bar, form, and tool bar, project window, tool box, properties box.
CE 210: Building Materials: 3 Units
Introduction and specification, cement manufacturing, cement types, cement specification, cement hydration, water for washing, mixing and curing, admixtures, wood, steel, bituminous materials, miscellaneous materials.
CE 211: Building Materials Lab: 1 Units
Aggregate tests specific gravity and absorption of fine aggregate, specific Gravity and absorption of course aggregates, abrasion Test for course aggregates using los angle machine, Density and void Ratio for fine aggregates, bulk density and void ratio for coarse aggregates, sieve analysis for fine aggregates, sieve analysis for coarse aggregates, cement tests (The fineness of cement, the normal consistence, initial and final time of set, density and specific gravity of cement), bricks tests (Compressive strength, Absorption test)
Ge 103: Workshop Engineering 2 Units
Classification of engineering materials. Properties and applications of important engineering materials. Primary manufacturing process: casting, welding, forging extrusion, drawing, rolling and metal joining. Basic measurements and inspection. Machining process: basic cutting tools, the centre lathe, basic operations, turning, taper turning, thread cutting and drilling. Engineering management, industrial safety and professional health. Training on using hand tools and production management and maintenance.
GE140: Engineering Mechanics I 3 Units
Introduction (Definitions, Newton’s laws, units), concurrent forces on a particle (Analyzing forces and determining the resultant of forces, concurrent forces in plane, concurrent forces in space), rigid bodies (Equivalent forces, principle of transmissibility, moment of a force acting on a rigid body about a point, moment of a force acting on a body about a giving Axis, moment of a couple reduction of a system of forces on a body to a resultant force only). Equilibrium of rigid bodies (Forces acting on a rigid body and structures, kinds of supports and reacting, drawing free body diagrams and calculating reacting), analysis of trusses, (Method of joints, method of sections), determining the centroid (center area) of certain area by dividing the area into certain area and by integration.
CE 240: Surveying I 3 Units
Basic principles of surveying, plan scales and ordnance of survey maps, linear surveying, simple optics, principal parts of survey instruments, leveling and vertical sections, contouring, random errors and theory of least squares.
Tw 307: Technical Writing and oral presentation 2 Units
Objective: The course is intended to develop the students’ ability on the oral presentation skills and to deal with concepts in scientific discussions and writings. It is to improve their concepts of Technical English enabling them to write Technical Reports, Technical essays as well as Business letters. The course lays stress upon the following areas of technical English:
- Different types of technical reports: The short informal report, the long informal report and the formal report; their format structure and style (Foreword and summary: Organizing main points for Non-specialist readers; Details or discussion: Organizing details for specialist readers; the abstract; conclusions and recommendations, etc.); Feasibility and project report; articles on technical topics and business letters.
- Technical terms of importance to engineering, with emphasis on spelling, and usage in sentences; technical terms used in computer applications.
- Symbols, abbreviations, glossaries, nomenclature, titles and sub-titles, tabular, graphical and pictorial presentation of data and the like, with examples.
- The course also abreast the students with concepts of research. The following main points are stressed upon: Selecting a suitable subject, writing a tentative thesis sentence, developing a preliminary bibliography, – Taking notes, writing précis and paraphrases, developing the first draft, preparing the final documentation notes, formatting the final draft.
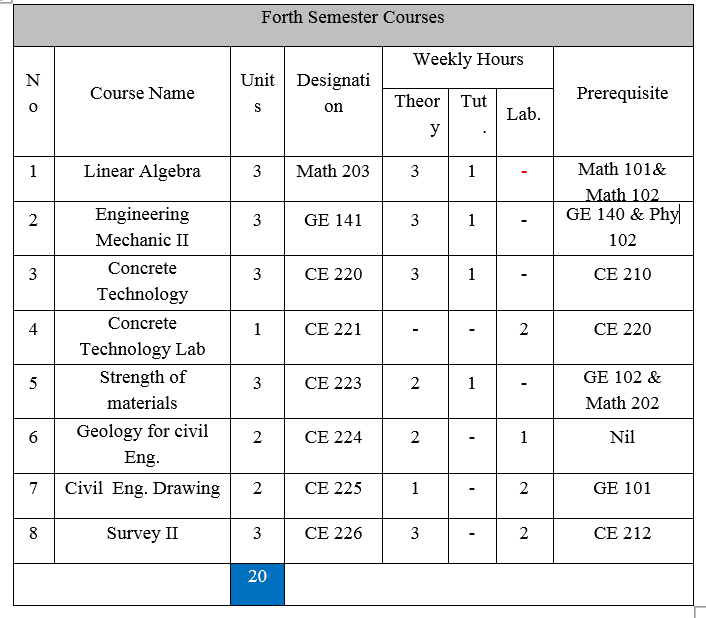
Math 203: Linear Algebra 3 Units
Vector spaces, matrices and determinants, simultaneous linear equations, linear transformations, Eigen value problems, canonical forms, numerical linear algebra, linear differential equations, linear programming, inner product spaces applications in various areas such as control theory, Statistics, linear circuit and vibration theory, etc.
GE141: Engineering Mechanics II 3 Units
Motion, velocity, and acceleration, uniform rectilinear motion, components of motion, relative motion , work and energy, impulse and momentum, mechanical vibrations, free and damped vibrations, forced vibration, static and dynamic friction.
CE215: Concrete Technology 3 Units
Definitions and classification, fresh concrete (Consistency, workability, bleeding), segregation of aggregate, hardened concrete strength (Compressive strength, tensile strength, shear strength, bond with reinforcement, factors affecting strength), elasticity, durability, creep and shrinkage of concrete. Mix design (Trial method, ACI method, British method)
CE216: Concrete Technology Lab 2 Units
Cement mortar tests (Compressive strength of cement mortar, tensile strength of cement mortar), fresh conceret tests (slump test, compacting factor test), hardened conceret tests (Cubic compressive strength, cylinderical compressive strength, split cylinder test), trial mix design, ACI method for mix design.
CE 220: Strength of Materials I 3 Units
Introduction and definitions, axial force, shear force and bending, moment in beams, engineering cross-section properties for structure members, determining of the centroid and second moment of area, simple stresses and simple strains, torsion of circular cross sections.
CE 249: Geology for Eng. 2 Units
Introduction, origin and structure of the earth, minerals and rocks, igneous, sedimentary and metamorphic rocks, different process on rocks, earthquakes and volcanoes, rocks deformation types, engineering, geological solution, geological engineering for major projects.
CE 300: Civil Eng. Drawing 2 Units
Introduction, the principle components of civil engineering construction, the components of building, footings, wall footing (Plain & reinforcement), isolated footing, combined footing (Rectangular and trapezoid), raft foundation with conversely beam (Up & down), piles footing, pier footing.
CE 241: Surveying II 3Units
Bearings, the direction of a line, theodolites, theodolite traverse, rectangular coordinates, tachometry, electronic distance measurement (EDM), curve ranging, horizontal and vertical curves, areas and volumes.
CE301: Fundamental of Electrical Eng. 3 Units
Kirchof’s laws and applications, network theorems, applied electromagnetism and magnetic circuits, rise and fall of currents, in an inductive circuits, capacitance, charging and discharging of capacitors, stored energy, alternating voltages and currents, average and R.M.S voltages, phasors complex notation, R-L-C circuits, self and mutual inductances, principle of operation and applications of transformers.
CE 221: Strength of Materials II 2 Units
Bending stresses in beam, design of beams for bending, bending about two principals axes with or without an axial force, bending about two not principal axes, shearing stresses in beams, composite beams (Analysis of composite beams using transformed section method, reinforced concrete sections), equivalent and principal stresses, normal principal stresses, Mohr’s circle of stresses (Analytical and graphical methods).
CE250: Fluid Mechanics 3 Units
Fluid properties, fluid presssure and its measurements, hydrostatics and its application, equilibrium of floating bodies, fluid masses subjected to acceleration, hydro-kinematics of fluids, Bernoulli equation and itsapplication, momentum equation and its application. Types and specifications of flow, flow over weirs, losses of total energy of the flow, steady flow in pipes, uniform flow through open channels, dimentional analysis, model analysis. Laboratory Part: Properties of fluids; statics of fluids; principles of continuity, Bernoulli, energy,and momentum; viscous effects; free surface flow.
CE 301: Construction and Architecture 3 Units
Introduction to building construction, architecture and its role, the factors that affected architecture (Climate, social, religion), types of buildings, architectural and structural details, damp proofing, sound insulation, heat insulation, finishing of walls and ceilings, doors and windows, means of moving between levels, stairs, lifts, ramps, moving stairs, joints in buildings, construction joints, expansion joints.
CE 303: Computer Aided Drafting in Civil Engineering 2 Units
Introduction to CAD, structure of AutoCAD, principles of drafting using AutoCAD , integration of AutoCAD and numerical modelling, application of AutoCAD to structural, highway, hydraulic and environmental engineering.
CE322: Theory of Structural I 3Units
General introduction (Structural analysis, loads on structures), analysis of statically determinate structures (Beams, frames, arches, trusses), deflections in statically determinate beams (Basic methods), deflections of statically determinate beams and fraames (Geometric methods (The moment area and conjugate beam methods), energy methods (Real and virtual work methods), deflections in statically determinate trusses.
CE 370: Soil Mechanics 3 Units
Simple soil properties, particle size distribution, sedimentation, Atterberg limits, soil classification, permeability and seepage, flow nets, compaction of soils, stress in soils, consolidation and settlement, shear strength of soil.
CE 371: Soil Mechanics Lab 1 Units
Moisture content, relative density, in-situ density, Atterberg limits, grain size analysis, standard and modified proctor test, California Bearing Ratio (CBR), consolidation, shear strength of soils, field collection of samples.
CE 323: Theory of Structure II 3 Units
Introduction to statically indeterminate structures (Advantages and disadvantages, method of analysis), analysis of statically indeterminate beams and frames using the consistent deformation method, analysis of trusses using the consistent deformation method, the three moment equation for the analysis of continuous beams and frames, buckling and stability of columns, visits to some building of architectural interest.
CE 328: Reinforced Concrete Design I 3Units
Review of properties of structural concrete and reinforcing steel, analysis and design of R.C beams using ultimate strength method, analysis and design of R.C. elements for shear, analysis and design of R.C. elements for torsion, bond, anchorage, and development length, design of continuous beams, short columns subjected to axial loads, detailing of reinforced concrete beams and columns.
CE 338: Ground Water Hydrology 3 Units
The hydrologic cycle, importance of ground water, source of ground water, types of layers containing ground water, ground water movement, sea water intrusion in coastal aquifers, wells, types of wells, design of wells.
CE 344: Highway Engineering I 3 Units
Introduction, vehicle characteristics, resistance and driving force, highway types, preliminary design and highway design procedure, geometric design of highways, horizontal alignment of highways, types of horizontal curves, sight distance, widening of carriage way on curves, vertical alignment, types of vertical curves, design of vertical alignment, planning of longitudinal super elevation in cross section, computation of earthwork, area of various cross-section, computation of volumes, intersection and interchanges types.
CE 457: Sanitary Engineering I 3 Units
Introduction; work of the sanitary engineer; water demand; domestic, public, commercial, industrial and fire demand; water quality; various sources of water; surface and ground water sources; water intakes; conventional water treatment processes; coagulation, flocculation, sedimentation, filtration (rapid and slow sand filters), and disinfection; hydraulic analysis of water distribution systems (Hardy cross method) and reservoir design; flow and characteristics of wastewater; design of a storm collection system; design of a sewerage system; introduction to wastewater treatment processes; physical, chemical and biological; introduction to biological wastewater treatment systems; activated sludge systems, tricking filters, oxidation ditches, stabilization ponds, septic tanks.
CE 476: Foundation Engineering I 3Units
Introduction to the footing, general principles of foundation design, types of footing, spead footing design, wall footing design, eccentrically loaded spread footings, combined footing design, cantilever or strap footing, tie-beams, raft foundation, settlement analysis of shallow foundation.
CE 429: Reinforced Concrete Design II 3Units
Analysis and design of one-way slab systems, analysis and design of two way slabs using ACI coefficient method, analysis and design of R.C. elemenet for torsion, columns subjected to axial load and uniaxial or biaxial moments, design of concrete sections subjected to tension without or with bending, staircase, design project.
CE 435: Design of steel structural I 3 Units
Introduction, types of steel structure, properties of steel, loads and specification, steel sections, limit state design, connections, design of tension and compression members, design of simply supported beams.
CE 445: Highway Engineering II 3 Units
Highway materials, soils, soil classification for highway purposes, testing of soil strength, soil stabilization, aggregates, requirement of a good highway aggregate, binder for highway construction, bituminous materials, testing of bituminous materials, bituminous pavement, component parts of highway pavement structure, types of highway pavement, preparation of sub grade.
CE 446: Traffic and transportation Engineering 3 Units
Traffic studies, purposes of traffic studies, information to be collected during traffic studies, traffic volume study, objects of traffic volume study, collection of traffic volume count data, representation of traffic volume count data, traffic control devices, types of traffic control devices, traffic signs, markings, and signals, advantage and disadvantage of providing traffic signals, original and destination, Urban transpiration planning, transpiration systems modeling, trip generation, trip distribution, mode split models, cost of highway transportation, present value concepts, operating expense, fixed and variable costs, rate of return, annual costs,
CE 477: Foundation Engineering II 3 Units
Design of retaining walls, introduction to deep foundation, pile foundation (classification of piles, description of pile types, structural design of piles, static pile capacity, single piles, dynamic analysis, pile load test, pile groups), walls for excavations, drilled piers or caissons.
CE 581: Eng. Management and Economy 3 Units
Management of project (Concept, stage of project management, network analysis), critical path method (Concept, stage of CPM, usage of liner program in critical path), project crashing, (Normal time, crashed time, normal time, crash coast), program evaluation & review technique (Concept, stages of PERT, usage of PERT, probability distribution, expected time), PERT/Cost control (PERT/Cost technique, stages of PERT/Cost, control, control of cost, project productivity approach), project scheduling (Loading leveling, limited resource model, heuristic methods), materials management, (Concept of materials management, important of materials management, objectives of materials management, functions of materials management).
CE 430: Reinforced Concrete Design III 3Units
Design of long R.C. columns, analysis and design of two-way slab systems using the ACI direct design method, deep beams, corbels, analysis of R.C. sections using working stress method, serviceability, deflections and cracking, design project.
CE 436: Design of steel structural II 3 Units
Beams, compound beams, crane beams, purlins, sheeting rails, plate girders, beam columns, slide column for a single story industrial building, crane columns, column bases, trusses.
CE 482: Construction Planning, Equipment’s and Methods 3 Units
Introduction, project planning and managements, project control during construction, factors effecting the selection of construction equipment, tractors and related equipment, scrapers, excavating equipment, loading, hauling, and lifting equipment, paving, compaction and finishing equipment, drilling and pumping equipment, piles and pile driving equipment, concrete form design.
CE 573: Soil Stabilisation 3 Units
Purpose of soil stabilization, mechanical stabilization, cement stabilization, asphalt stabilization, lime stabilization, chemical stabilization, preloading and vertical sand drains, reinforced earth, reinforced retaining walls, stabilization by heating, grouting, blasting, compaction of granular soils.
CE 583: Specification and Contract 2 Units
Legal aspects of construction contracts, classification of contracts, types of contracts, general and special conditions of contracts, claims and dispute resolution, standard contracts, specification of construction materials, standards, common used standards, quantity surveying for civil engineering work, estimating of construction prices and costs.
CE 598: Project methods and proposal 2 Units
Oil field methods, data gathering, sampling methods, data preparation and classification, data presentation, spread sheets calculation and analysis of data, project proposal methods, referencing methods, software’s practices, project methods, and project report structure, project writing formats, project proposal preparation and presentation.
CE 599: Graduation Project 4 Units
The class objective is to provide experience in the application of engineering principles to the solution of a specific problem in Civil Engineering. Students are required to select a topic and prepare a proposal, including a work programmed for a project to be undertaken under the supervision of a faculty member. Projects may include laboratory or field experiments, design problems, computer analysis or literature reviews. Students are expected to prepare a typewritten report and to make an oral presentation of their project.
